
LONG TERM MEMORY TWO MAIN TYPES: Declarative: (we call this up from memory as we need it) Episodic memory of our own lives Semantic knowledge of language, words, meanings Procedural involves skills acquired thru life eg. The process of forming a memory involves encoding, storing, retaining and subsequently recalling information and past experiences. There are three main distinctions among different types of memory: Implicit vs. STM contd The PRIMACY-RECENCY effect: Recalling info at the beginning or end is easier How does this relate to working memory? They are similar, but working memory also includes info stored in long term, brought into consciousness for processing working memory is necessary for the control of attention (Klingberg, 2008). We store different types of information (procedures, personal experiences, facts, language, etc.) in our long term memory. DDT, COMSAT, phone #s, or to remember a list of thingsfigs, lettuce, oranges, apples, and tomatoesmake a word out of the first letters (e.g., "FLOAT") - acronyms 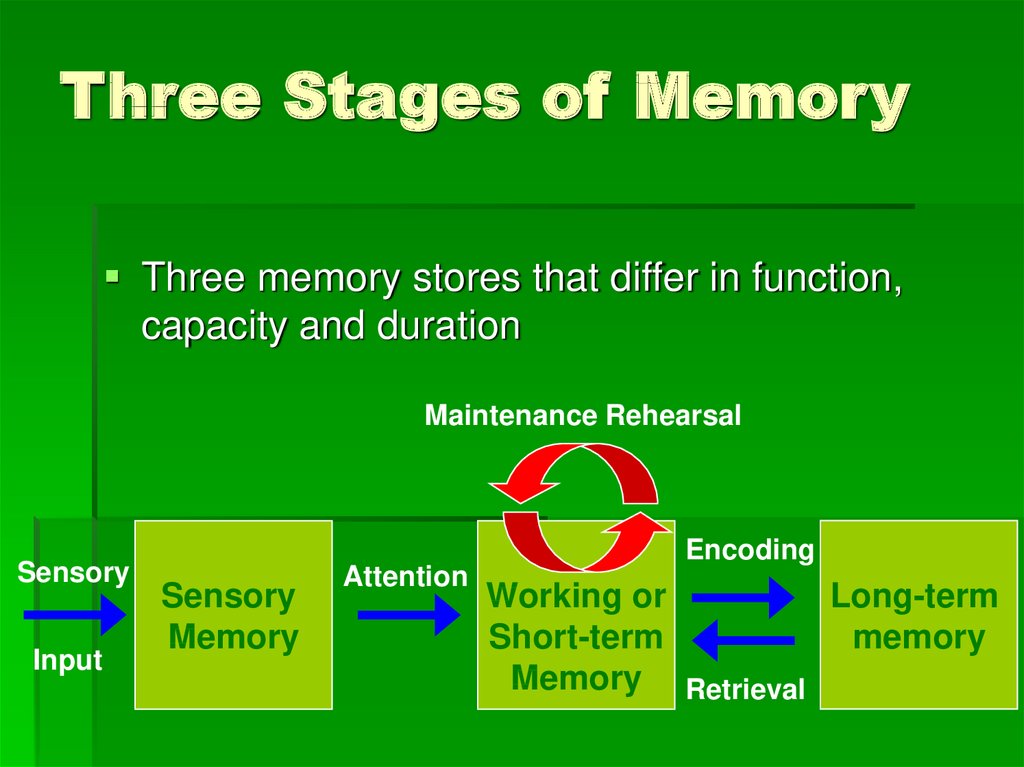 SHORT TERM MEMORY Definition & durationCapacity & chunking Things you have in conscious mind at any one moment To retain longer than a few seconds, we must use techniques like maintenance rehearsal (repeating the info to self) Lasts about 20 seconds without rehearsal Can hold ~ 7 unrelated items Each item can consist of a collection of other items, but if they are packaged into one chunk they count as 1 Eg. Sensory Memory Sight and hearing hold an input for fraction of a second Psychologists refer to 2 types of SM: auditory sensory memory = echoic memory, and Visual sensory memory = iconic memory Sensory mem serves 3 functions: 1. TIP: You can think of the three stages of memory processing in the following way: encoding is like listening to songs, consolidation is like recording those songs (or burning a CD), and retrieval is like playing back the songs Retrieval Bringing info from LTM storage into working memory (STM) How easily this happens depends on how efficiently it was encoded, and also on how many sense were used while encoding. Storage The process of maintaining info in LTM over a period of time How well this works depends on how much effort was put into encoding it. Each type of memory is used to store different types of information: 1. There are three types of memory that are important to learning and they are your working memory, short-term memory, and your long-term memory.
SHORT TERM MEMORY Definition & durationCapacity & chunking Things you have in conscious mind at any one moment To retain longer than a few seconds, we must use techniques like maintenance rehearsal (repeating the info to self) Lasts about 20 seconds without rehearsal Can hold ~ 7 unrelated items Each item can consist of a collection of other items, but if they are packaged into one chunk they count as 1 Eg. Sensory Memory Sight and hearing hold an input for fraction of a second Psychologists refer to 2 types of SM: auditory sensory memory = echoic memory, and Visual sensory memory = iconic memory Sensory mem serves 3 functions: 1. TIP: You can think of the three stages of memory processing in the following way: encoding is like listening to songs, consolidation is like recording those songs (or burning a CD), and retrieval is like playing back the songs Retrieval Bringing info from LTM storage into working memory (STM) How easily this happens depends on how efficiently it was encoded, and also on how many sense were used while encoding. Storage The process of maintaining info in LTM over a period of time How well this works depends on how much effort was put into encoding it. Each type of memory is used to store different types of information: 1. There are three types of memory that are important to learning and they are your working memory, short-term memory, and your long-term memory. 
And 3 PROCESSES of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Encoding: transforming info so the NS can process & store it We use acoustic codes when we try to remember something by repeating it out loud We use visual codes when we try to keep a mental picture Semantic codes trying to remember by trying to make sense of something Understanding Different Functions of Memory. Answer (1 of 4): The Analytical Engine, designed by Charles Babbage in the mid-1800’s but never built, was to use geared disks, each containing the digits 09 on them, in tall stacks.

However, some choose to opt for a 64GB to 128GB card just to have extra space.
THREE TYPES OF MEMORY PICTURES PORTABLE
3 TYPES OF MEMORY: Sensory Memory Short Term Memory Long Term Memory An 16GB to 32GB card is big enough for most portable memory purposes.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
